Modern SEO is focused on the intent and meaning behind content.
When I first started off in SEO in 2006, optimizing for Google (+Yahoo & MSN/Windows Live) was mostly about keyword density ratios, link counts and other tricks like keyword stuffing then hiding the text with the same color as the background. Page Rank sculpting was also another effective technique at the time, that involved adding nofollow tags to internal links to preserve more link juice for certain pages. There was no greater feeling than to see our sites reach #1 rankings after making one update. Looking back 20 years later, those days were fun but none of those strategies served the user at all.
The Evolution From Keyword Stuffing to Semantic Search
I’ll list a brief timeline over the years for major Google updates that have shaped the direction of how SEO is today. I’m by no-means an expert on every single Google algorithm update but these are some well-known ones that have changed the industry from keyword stuffing text on the same color background to today’s intent-based content.
- 2011: Google Panda – Targeted low-quality content and improved the quality of search results.
- 2012: Google Penguin – Targeted spammy link building practices and penalized websites with manipulative backlink profiles.
- 2012: Exact Match Domain Update
- 2013: Google Hummingbird – Introduced a new search algorithm focused on understanding user intent and context.
- 2015: Mobile-Friendly Update – Prioritized mobile-friendly websites in mobile search results.
- 2015: RankBrain – Introduced machine learning to better understand search queries and deliver relevant results.
- 2019: BERT Update – this was arguably the biggest shift in how Google search works in that exact match keywords & lexical search were greatly de-emphasized in favor of user-intent and semantically-relevant content.
- 2022: Helpful Content Update – Targeted sites created solely to boost search rankings, penalizing them and promoting useful and original content.
- 2024: Site Reputation Abuse – ahem, Forbes Advisor.
I remember competing against a California photography website over several years. I could never outrank this site. It would drive me crazy that this site’s content was littered with keyword-stuffed gibberish on the page. While some of the sentences on its’ own might somewhat make sense, put together into the context of a paragraph the content made zero sense.
Here’s an example of what I was competing against 20 years ago. The site is no longer active but I got this from my ex-competitor’s homepage on The Wayback Machine:
Photo collection of California pictures is provided for professional stock photos in California. Photography of California coast, stock photos of Southern California national recreation area California pictures, stock photo gallery. California coast photography stock photos of mountains Pacific Coastal valley’s view pictures of mountains in fog, Ventura County photo gallery Southern California coast photo gallery of California beach photos, California beach sunset photos, beach pictures. California national and state park stock photos of Southern California coast.
Every page was filled with copy like this. Believe it or not, this type of garbage “content” could easily rank #1 on Google. People complain today about Reddit results dominating the SERPs and the proliferation of AI-generated content, but today’s content is infinitely better than a lot of what was ranking 20 years ago. I don’t know how much business if any these types of sites were getting through the use of that content but if I see a site with keyword-stuffed gibberish that doesn’t exactly scream legit to me. Google has made a lot of controversial updates over the years, particularly since the Helpful Content updates of 2022 but for the most part the SERPs are more useful than they were in the 2000s through early-2010s.
Semantic Search
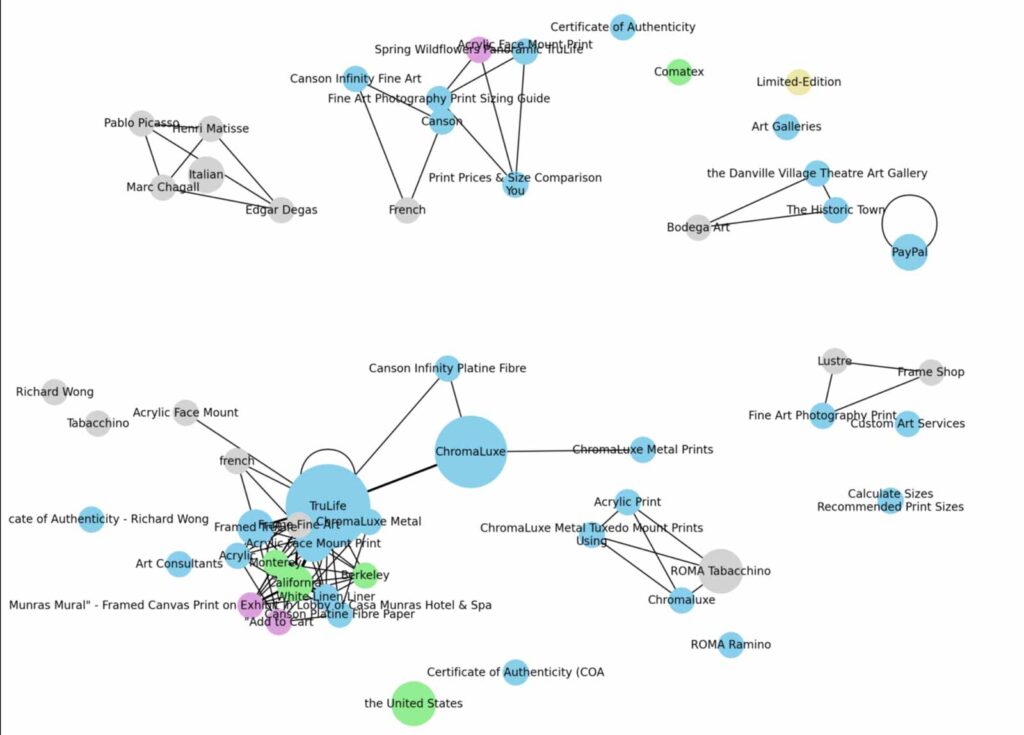
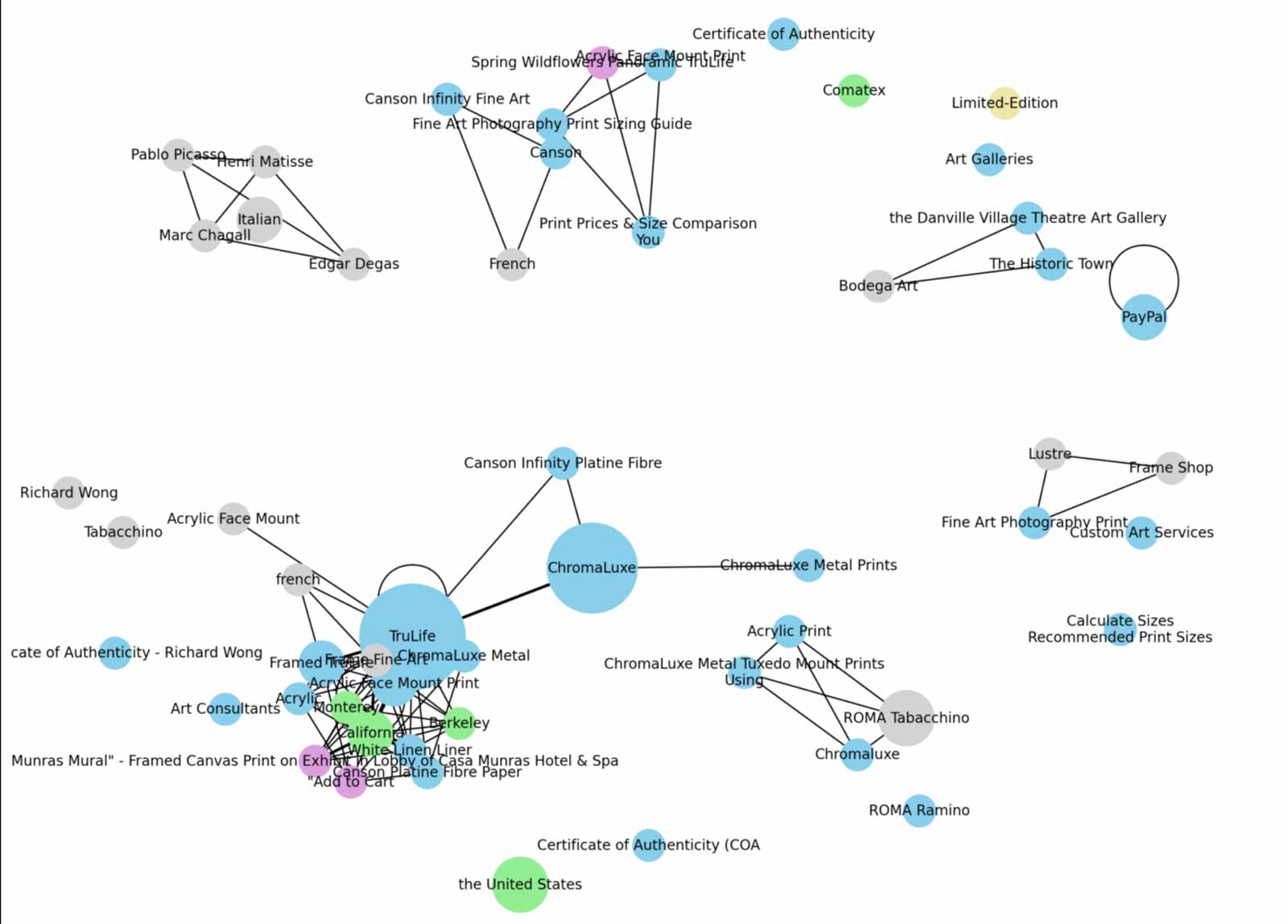
Fast-forward to 2025 and we’re now talking about natural language processing (NLP), vector embeddings and entities. This is basically a fancy way of saying machines need to convert words into a mathematical equation in order to understand the meaning of text then connect them to a database of information. For the average person, it means you should write naturally for humans but know that a machine needs to understand your content as well if you want SEO or AI search traffic. Being clear and direct is important as machines as well as some people may have a difficult time understanding more abstract language. The SEO part is in understanding what it is that people want to accomplish through their search and what it is they are searching for then using that to inform the content. But the days of exact match keyword-stuffing are long gone.
Semantic SEO Tools
Most SEO tools are still stuck in the old-school way of individual keyword rankings and search volume data. This is why I have been spending time on building my own semantic SEO tools built on NLP and data visualization to analyze website content. SEO is a complex and rapidly evolving industry so being able to adapt with the times is important. Not every site would necessarily benefit from this approach such as competitive e-commerce verticals but when it comes to content-heavy verticals this is absolutely the approach needed to succeed.